Terminologies in Astronomy:
1. Apsides (Apogee, perigee), aphelion, perihelion
Apogee: Farthest part of orbit around Earth
Perigee: Closest part of orbit around Earth
aphelion, perihelion ~ around the Sun, farthest and closest respectively.
apocynthion, pericynthion for around the Moon, farthest and closest respectively.
There are also terms for other objects (Check Wikipedia) such as Mercury, Mars, stars, etc.
Wikipedia illustrations:
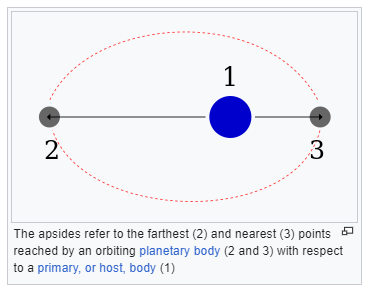
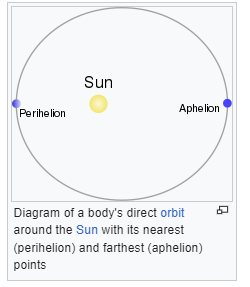
2. Conjunction: When two objects are close (within 6 degrees) as seen by viewer.
Inferior conjunction: When primary object is in front of the second (ie. the Sun)
Superior conjunction: When primary object is behind the second
Opposition: When primary is directly opposite to the second (ie. the Sun) from the viewer's point.
3. Greatest Elongation
Greatest eastern elongation: When inner planets (Mercury, Venus) are furthest away from the Sun as viewed from Earth, going into inferior conjunction with the Sun.
Greatest western elongation: When inner planets (Mercury, Venus) are furthest away from the Sun as viewed from Earth, going away from inferior conjunction with the Sun.
4. Eastern/Western Quadrature: For example, when the Moon and the Sun are 90 degree from Earth. Eastern quadrature is the time of first quarter of moon phase, western quadrature is the time of last quarter.
Wikipedia's illustration:
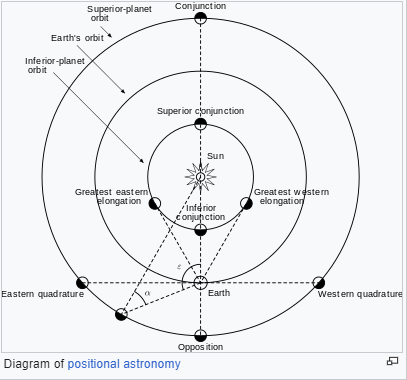
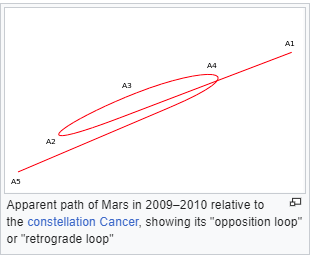
5. (Apparent) Retrograde Motion: When object's path does a little backward and forward (prograde) during opposition.
Wikipedia illustrations:
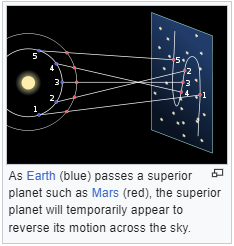
6. sub-lunar point, antipodal point: Tidal pull on the Moon's side, tidal rise on the opposite side, respectively. Tide at antipodal point is caused by the Moon pulling the Earth.
7. (Lunar) Libration: The reason we can see more than 50% of the Moon from Earth. Longitude due to eccentricity of lunar orbit; Latitude due to axial degree of lunar rotation. And diumal libration is when an observe observes from one side of Earth to another along Earth's rotation.
Earthsky illustration:
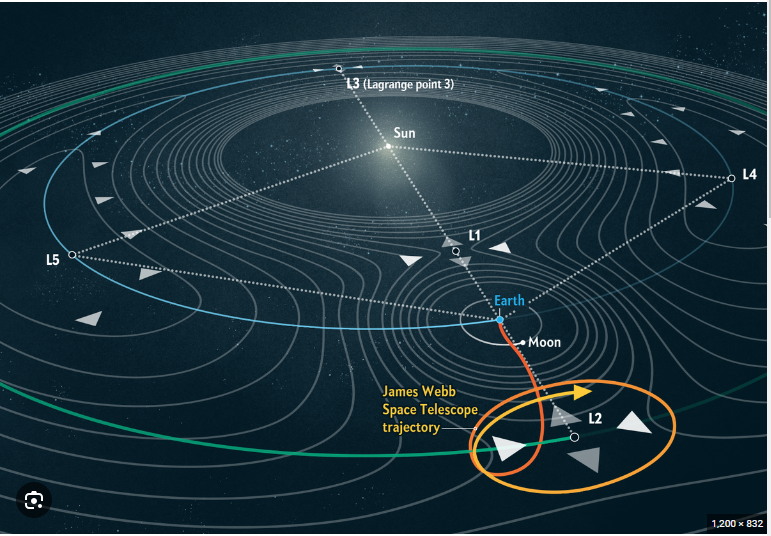
8. Lagrangian point (L-point, Lagrange Points): L1 (between Earth and the Sun), L2, L4, L3, L5 (plotted counter-clockwise from the right of Earth, if the Sun is on the Left).
Scientific American Illustration:
9. Occultation: When an object passing in front of another.
Transit: When the object is small
Eclipse: When the object is big
11/11/2009 Edit
10. Moon Phases: New moon, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full moon, waning gibbous, third quarter, waning crescent.

Ecliptic: The path of the Sun before the background of the stars as seen from Earth.
A model structured to show the orbits of planets in the solar system.