Resources according to WTS syllabus (Latin by Professor Rester's):
Free online: https://www.textkit.com/greek-latin-forum/viewtopic.php?f=6&p=213636
GREEK
Easy to understand tutorial on Greek: https://www.ntgreek.org/learn_nt_greek/inflect.htm
LATIN
Learn to Read Latin by Andrew Keller
Second Latin: Preparation for the Reading of Philosophy, Theology and Canon Law by Scanlon
Modern Greek Keyboard Layout:

Alphabet:
Alpha - Α α, Beta - Β β, Gamma - Γ γ, Delta - Δ δ, Epsilon - Ε ε,
Zeta - Ζ ζ, Eta - Η η, Theta - Θ θ, Iota - Ι ι, Kappa - Κ κ, Lambda - Λ λ,
Mu - Μ μ, Nu - Ν ν, Xi - Ξ ξ, Omicron - Ο ο, Pi - Π π, Rho - Ρ ρ,
Sigma - Σ σ/ς, Tau - Τ τ, Upsilon - Υ υ, Phi - Φ φ, Chi - Χ χ, Psi - Ψ ψ, Omega - Ω ω
Films used in learning Greek:
Maestro, by Christoforos Papakaliatis, on Netflix

Latin lesson:
I shall attempt first with Benjamin L.D'Ooge's Latin for Beginners, available on archive.org, referenced by textkit.com.
Latin Dictionaries:
Online-Latin-Dictionary
Latin-Dictionary.net
Latin is Simple
For Grammar:
The six cases of nouns:
Nominative: Used for the subject of the verb.
Vocative: Used to call or address someone or something.
Accusative: Used for the object of a verb.
Genitive: Used for nouns that are ‘of’ something else and to show possession (who something belongs to).
Dative: Used for nouns that are to or for something.
Ablative (absent in Greek): Used for nouns that are by, with or from something.
Dative: Ego litteris Latinis (plural) studeo (intransitive). (I study Latin Literature)
Accusative: Ubi litteras Latinas (plural) legitis (transitive)? (Where do you read Latin Literature)
Demonstrative Pronouns:
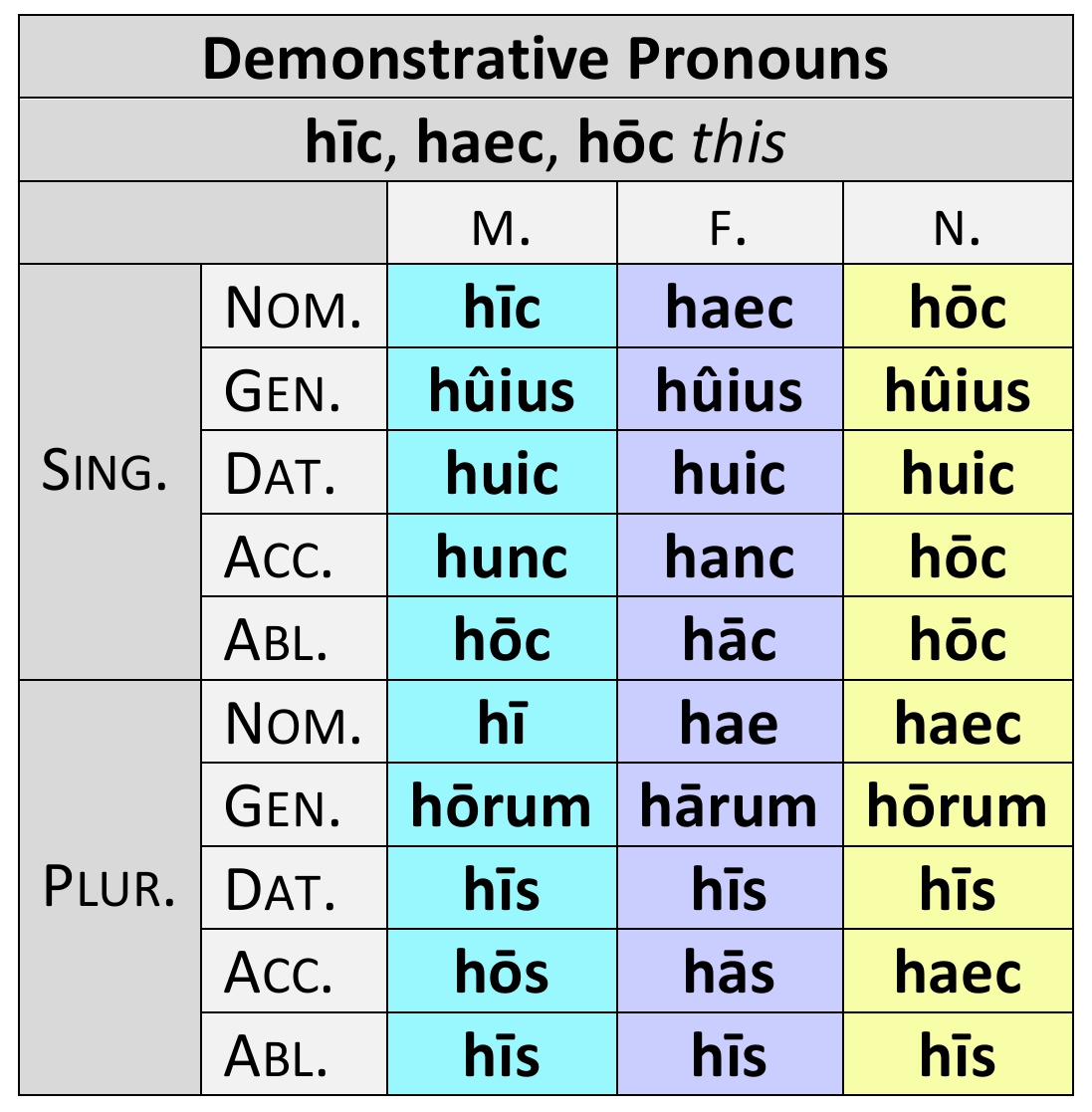
This: hic, hoc haec
Hic = Masculine singular nominative
Hoc = Neuter singular nominative, Accusative, Ablative
Haec = Feminine singular nominative
Greek (modern):
Ο άντρας, η γυναίκα, το νερό
The in masculine, feminine and neuter.
The indefinite article changes accordingly: Masculine: ένας (énas) Feminine: μία (mía) Neuter: ένα (éna)