A supposedly well made 100 episode documentary. Forwarded from mom.
中華通史100集.由古至今的朝代興衰,可以看看參考。
https://www.kunlunce.com/llyj/fl11111111111/2018-07-07/126406.html
For some reason, the idiots at YouTube removed the CCTV6 account, and thus the English subbed series is gone. Good thing I downloaded the whole thing long ago.
Youtuber: Learn Chinese Now also has interesting take on identifying Chinese Dynasties in Movies (Accented Cinema, another youtuber also did something similar with China History and movies):
Part 1
Part 2
只要花75小時,即可看盡中國四千年歷史的興衰,非常非常值得。全部100集都在這裡了,按照目錄,想看那一集,隨挑隨看。
CCTV6紀錄片《中國通史》目錄:
第01集 中華道路
第02集 中華先祖
第03集 農業起源
第04集 文明起源
第05集 邦國時代
第06集 夏王朝覓蹤
第07集 殷商興亡
第08集 商代文明
第09集 武王克商
第10集 周公攝政
第11集 周王室的衰落
第12集 春秋爭霸
第13集 孔子
第14集 列國變法
第15集 戰國七雄
第16集 諸子百家
第17集 秦國崛起
第18集 秦始皇統一中國
第19集 楚漢戰爭
第20集 郡國並行
第21集 文景之治
第22集 漢武帝
第23集 兩漢經學
第24集 昭宣政治
第25集 王莽改制
第26集 光武中興
第27集 絲綢之路
第28集 清議與黨錮
第29集 黃巾起義
第30集 三國鼎立
第31集 諸葛亮治蜀
第32集 西晉統一
第33集 魏晉風度
第34集 門閥政治
第35集 梁武帝治國
第36集 孝文帝改革
第37集 北周武帝
第38集 陳朝興亡
第39集 魏晉佛教
第40集 再造統一
第41集 煬帝功過
第42集 貞觀之治
第43集 武則天
第44集 開天盛世
第45集 安史之亂
第46集 中晚唐的困局
第47集 世界都會長安
第48集 吐蕃興衰
第49集 敦煌
第50集 唐朝的對外關係
第51集 唐代宗教
第52集 五代十國
第53集 宋太祖
第54集 澶淵之盟
第55集 與士大夫共治天下
第56集 王安石變法
第57集 靖康之難
第58集 宋金和戰
第59集 偏安東南
第60集 東京夢華
第61集 宋代新儒學
第62集 宋代文化
第63集 契丹興起
第64集 西遼建國
第65集 完顏阿骨打
第66集 金朝興亡
第67集 遼金文化
第68集 西夏興亡
第69集 蒙古興起
第70集 忽必烈大帝
第71集 兩都巡幸
第72集 大元帝師八思巴
第73集 海上絲綢之路
第74集 馬可波羅與中國
第75集 元順帝
第76集 明太祖朱元璋
第77集 永樂遷都
第78集 鄭和下西洋
第79集 內閣制度
第80集 土木堡之變
第81集 王陽明心學
第82集 海疆與互市
第83集 張居正改革
第84集 耶穌會士來華
第85集 江南市鎮
第86集 白銀資本
第87集 崇禎帝
第88集 入主中原
第89集 王朝的穩固
第90集 收復台 灣
第91集 統一大業
第92集 軍機處
第93集 攤丁入畝
第94集 文治與文字獄
第95集 被動的自強
第96集 鴉片戰爭
第97集 太平天國
第98集 甲午戰爭
第99集 維新與革命
第100集 帝制的終結
Supplement: Where did China get its name:
Chinese ancient concept of the world: 天下, surrounded by 4 barbarian/foreign culture 四夷 (西戎,北狄,华夏,东夷,南蛮). 华夏=神州 (divine state), 九州 (of the time). 中国:used by Song Dynasty (960-1279 AD).
The word "China", 1. Possibly based on the word Qin, from Qin Dynasty reforms. 2. India's name for the silk country Sina of 夜郎 (Zi-na) from 荆 (jing-a) of 楚国. 3. Jin Dynasty (晋朝) 300AD.
I'm adding a chart with China Dynasties timeline:


Episode 01: 中华道路 (summary of the entire history in first episode)
800BC - 200 AD 轴心时代 (Axial Age): Era of philosophers, Western terminology coined by Karl Jaspers: Axial Age. Eastern: 百家争鸣。An age of huge global changes in philosophy = 8th century to 3rd century BC.
墨子 (468?BC - 376BC): Developed Mohism.「兼愛 unbias/universal love」、「非攻 against war」激进的救世思想 (不同于老庄:清静无为,顺应自然的政治思想)
Also against Confucians' benevolent love 仁爱 (different degrees of love based on family & social status).
兼愛:没有任何亲疏贵贱的爱。非攻:反对战争。
@4:32 风尘仆仆:形容旅途奔波,忙碌劳累
老庄 (道家),是老子 571-471BC 和庄子 369-286BC 的并称 为道家:主张清静无为 (指一切听其自然,人力不必强为。 出自《谏作玉清昭应宫》)
Philosophy of same era:
- Chinese philosophy on categorizing change into two categories as 阴阳五行 (阴阳家)。
阴阳家:变化归结于阴阳五行:阴阳,指世界上一切事物中都具有的两种既互相对立又互相联系的力量;五行即由“木、火、土、金、水”五种基本物质的运行和变化所构成。 - 法家:春秋战国时期 770-256BC 以法而治
- 纵横家:战国秦汉 475BC-220AD 游说各国
All schools of thoughts are connected to one pillar: 儒家 - 孔子 551-479BC。How to 人成仁: 以人义,礼乐,德治教化为基本内容。
儒学didn't get picked up not only in Confucius' time, but also not even 100 years later in 孟子's time. Next is 荀子's student: 李斯,主导焚书坑儒 buring of books under Emperor Qin 213BC. 【中国历史上的四次焚书浩劫:秦孝公焚书 359BC,秦始皇焚书 213BC,梁元帝焚书 508-554,乾隆皇帝焚书 1773-1782】
A classic art collection about Confucius Bio by unknown artist was 孔子圣迹图三十六幅. 孔子一生颠沛流离( 形容生活艰难,四处流浪)。
汉朝开国皇帝刘邦 (202-195BC):first historical record of ruler publicly worship/paying tribute to Confucius. (18 years after Qin's 213BC books burning)
True revival of 儒家: 60 years after Han Dynasty, 汉武帝时代 (156-87BC 西汉第七位皇帝). 大儒 董仲舒: 罢黜百家(not getting rid but actually uniting the essences of all schools),独尊儒术
佛教在东汉后期 (184-220) 开始传入中国。
[Learn 唐宋元明清]
明朝:王阳明 16岁 儒 释(buddhist) 道 天才。Not limited by previous 程朱教条。Introduced:知行合一。阳明心学。儒家的更新。
361 B.C. Master in legalism: 商鞅. Praised by 秦孝公 of 秦国. Promoted legalism. 秦始皇 统一六国, 138 years after his reformation. However, 严刑峻法 caused the dynasty to finish 15 years later. Conclusion: 不能单靠以法治国。
89 B.C. 汉武帝 in trying to figure out why 以礼治国,以法治国 don't work out well, published 轮台诏: 以明休息,思富养民的国策。
隋朝(Sui Dynasty very short lived 581-618AD):Strict edict of 三省六部制
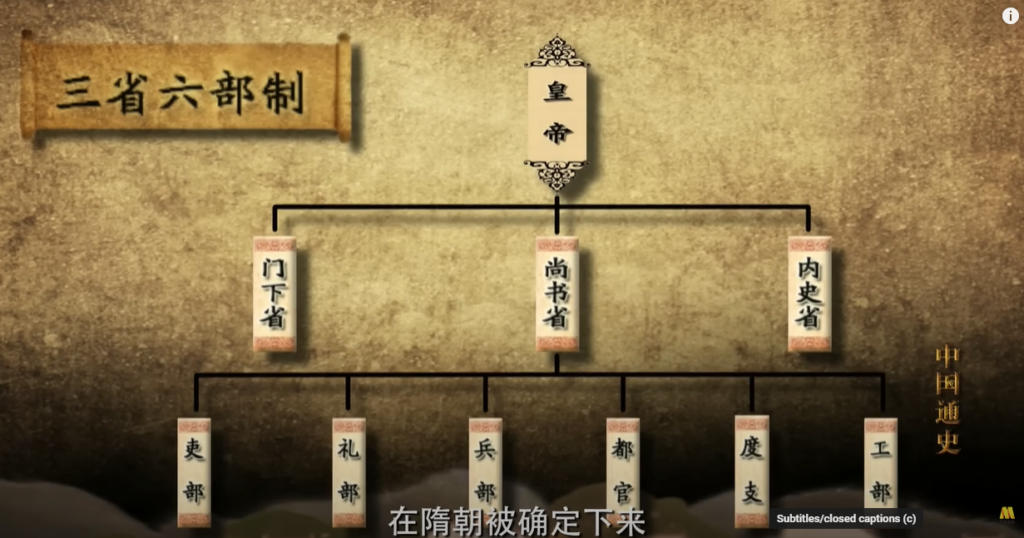
began 科举考试 (Imperial examination - becoming government officials through examinations) Great talents chosen.
唐王朝 (618-907AD):See 十八学士图,二十五学士图,八公图卷,丝绸之路 绢本 谢振瓯。
However,封建制度 (Feudalism) will ultimately fail, because it's 专制主义 (absolutism, despotism, dictatorial). When the king is corrupted, no matter how good the system is, it will all collapse.
The 五代十国 (907-960) was an era of 兵变(mutinies)与政变(coup d'etat), ended with 赵匡胤 (founder of the Song Dynasty 960-1279, via mutiny of 陈桥 - 陈桥驿兵变, Song Taizu - 宋太祖), the alleged founder also of the 太祖长拳。Using a large group of 文臣 (civilian court officials) and 士大夫 (scholarly officials) of important roles, to suppress 武夫悍将 (powerful knights and generals).
明朝 的 朱元璋 fought against the kind of corruption he experienced in 元朝. He applied harsh punishment with no mercy: capital punishment to officials' greed, almost no officials left in court. Very effective, but short lived.
*** Back to earlier history: 三千年前的重要占卜 (fortune telling/divination) ***
1046 BC - 周武王集结大军即将出兵伐商 (preparing to attack Shang regime) in a time of great reliance upon divination. However, Zhou Wu attacked despite being shown bad omen (不吉利的兆象), faced bad weather, obtained victory. And thus, 冲破了夏商 (Xia & Shang) 的迷信天命观. Zhou (周礼) focused on ethics 伦理 and morality 道德. 武王伐纣 (King Wu attack Zhou regime) = 摆脱天命 (against "heaven's" will). 改变天命观、世界观。
133 BC - 汉武帝 attacked 匈奴 (the Huns) during Han Dynasty (202 BC - 220 AD). Because in the first 60+ years, the Han Dynasty was turmoiled under the Huns. But the Huns knew the plot, 马邑之谋 was a failure. But 汉武帝 persisted, heroes such as 李广,卫青,霍去病, etc. emerged. After 3 more battles, the Huns were defeated.
138 BC - 中华民族并不是好战也不是保守的民族。丝绸之路便是由中国人开拓出来的, by 张骞.
汉唐时期 - 海上丝绸之路.
1405 - 1433 AD 郑和下西洋.
To be continued @33:00 (my video)
